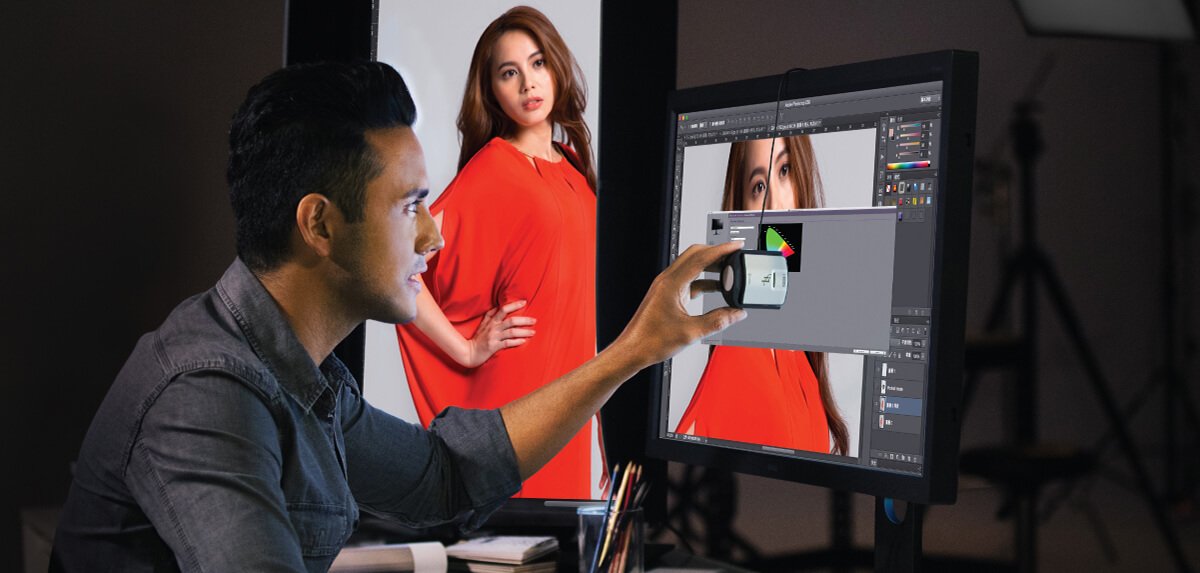
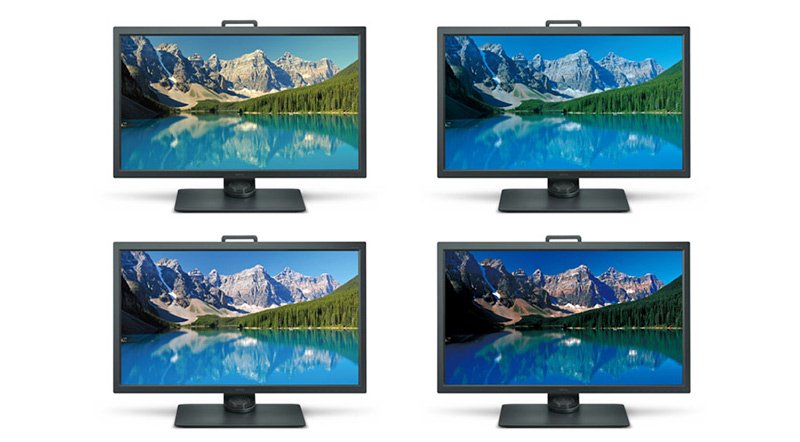
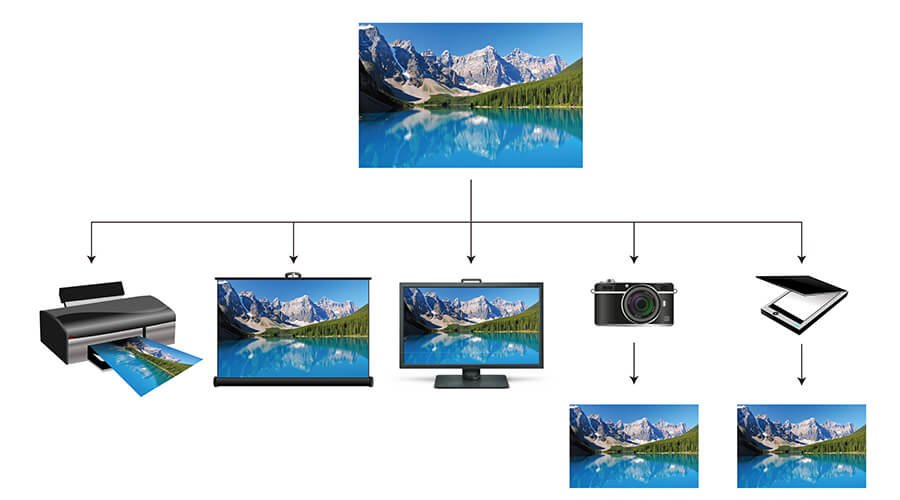
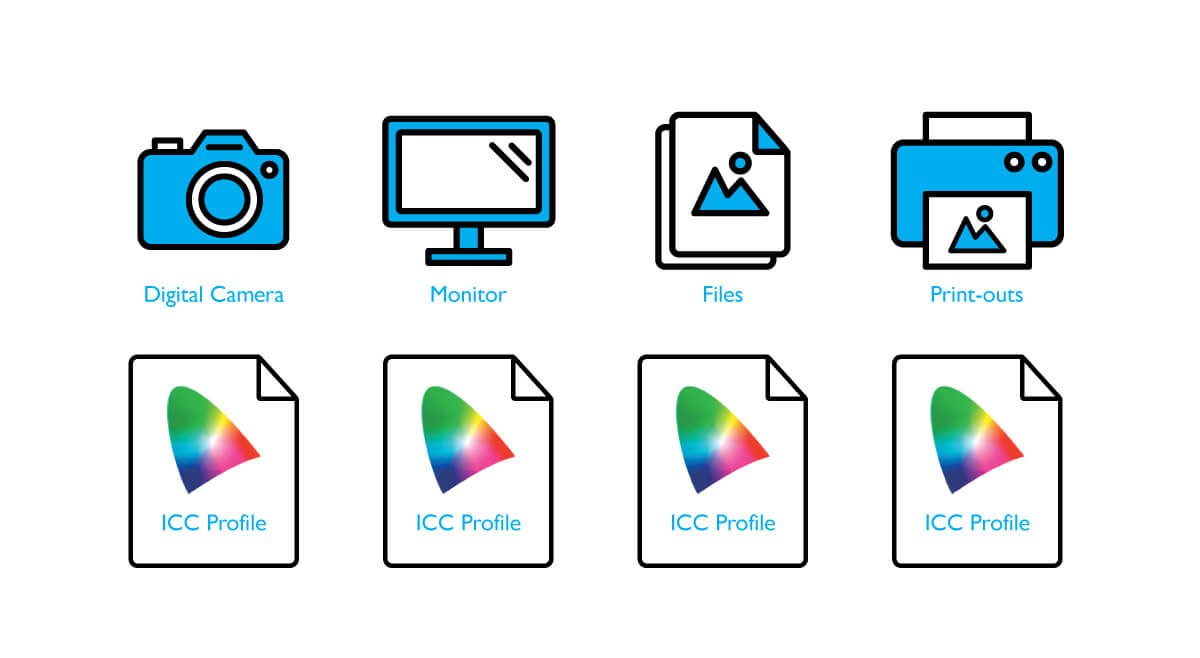
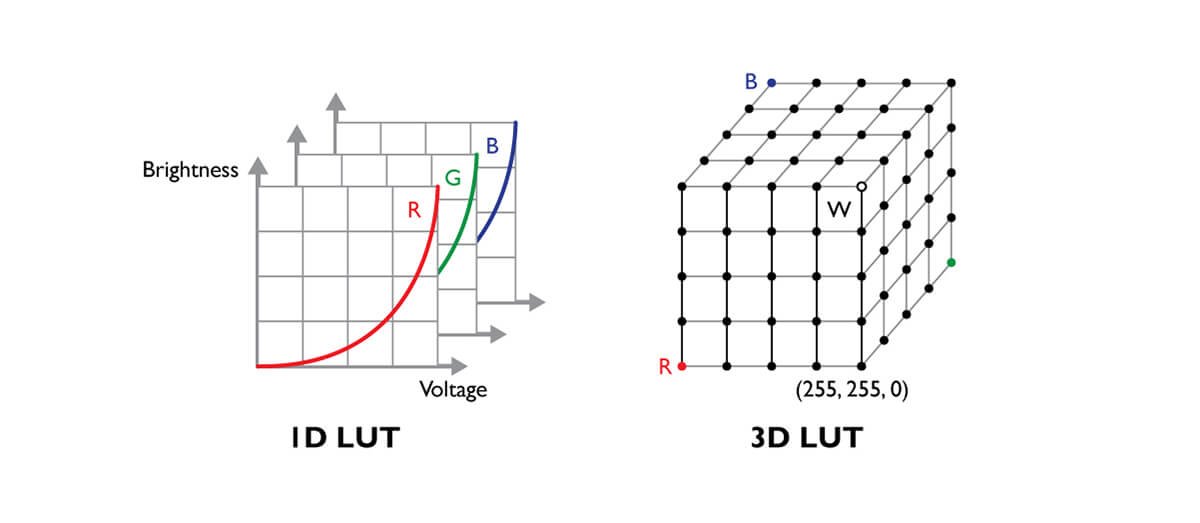
Before explaining 3D-LUT, let’s first understand what LUT is. The full name of LUT is Look-Up Table. Its main function is to interpret the color signal from the computer, find the corresponding output value in the Look Up Table, and then display the result on the monitor. We all know that an image is composed of many dots (pixels), and the information (bit depth) recorded in each pixel consists of color information. In the monitor world, LUT is used as an index. The corresponding new values are found from LUT and then displayed. The advantage of this is that it can display the colors more efficiently. The biggest difference between 3D-LUT and traditional 1D-LUT is that the latter finds the corresponding color values (R, G, B) in three one-dimensional Look-Up Tables of R, G and B individually, and the index source of 3D-LUT is a three-dimensional color combination chart, and corresponding values are found from within. Its greatest advantage is that it can display the correct colors more accurately.